Ceramic Processing
1. Introduction:
We are manufacturers and suppliers of technical ceramic materials and components. Our products, manufactured to our customers’ specifications, are utilized across various industries for thermal insulation, electrical insulation, abrasion resistance, chemical, and industrial applications.
We distinguish ourselves by providing customer support for the technical specifications of their complex ceramic products. We offer comprehensive design and manufacturing services.
2. What is Ceramic Processing?
Ceramic processing involves the manufacturing and processing of products from ceramic materials. The outstanding properties of ceramics have ensured their extensive use over many years and remain highly significant in modern technology. Thus, they are well-suited for various applications such as construction, automotive, refractory materials, power generation, industrial, chemical, and food processing.
3. Ceramic Processing Methods:
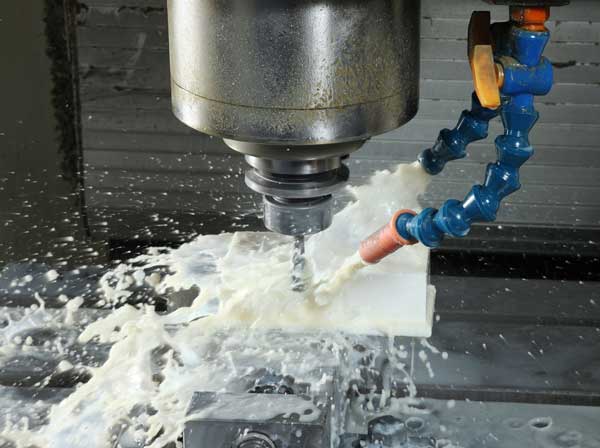
CNC Milling: Ceramic materials are processed using milling methods. Ceramic is a non-metallic material, often composed of oxides such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), zirconium oxide (ZrO2), and other compounds like silicon carbide (SiC). Ceramic materials exhibit high mechanical, thermal, and chemical resistance properties and are commonly used in applications requiring high durability, heat resistance, and electrical insulation.
Ceramic processing demands high precision and specialized milling techniques due to ceramics’ harder and more brittle nature compared to metals.
Tools for Ceramic Milling: Hard carbide milling cutters or other reinforced materials are typically used to withstand pressure and cut through ceramic materials.
4. Factors Affecting Ceramic Processing:
Temperature differentials during processing and high cutting pressures can lead to issues such as cracking, chipping, and tool wear. Therefore, ceramic milling is often performed using specialized machining equipment and requires strict control during processing.
Processing zirconia ceramics after sintering is essential in preparing solid materials for various applications. Challenges in processing zirconia ceramics mainly arise due to its exceptionally hard nature, akin to that of steel. The flexural strength and fracture toughness of zirconia ceramics are somewhat affected by heat addition or temperature rise. This characteristic demands the use of high-speed cutting tools at speeds ranging from 500 m/min to 670 m/min.
5. Applications of Ceramics:
Ceramics are commonly used in various industries, including medical, electronics, automotive, and aerospace. For instance, in the medical field, ceramic materials are used to manufacture parts such as artificial valve cores, dental prosthetics, and ear cups. In the automotive industry, ceramics are also used to process corrosion-resistant parts and thermal insulating components in engines.
 EN
EN
 VN
VN









